Everyone wants their website to be successful, attract visitors and ultimately convert sales. Just because you have a website does not mean you are going to be successful. First you need to be found. And to be found means ranking high in search results. In order to rank high, your website needs to be optimized. Below we will be talking about the 16 key components of on-page optimization.
Who Needs to Find You?
Your website needs to be found by your customers and in order to be found, you must be in the top rankings. In order to get there, there is one and only one top client you want to found your website.
Most people will say “I am looking for people who will buy” or something like that. You are right, but also very wrong.
The real answer is Google. If you do not structure your website the way Google and other search engines want, you will not get the top rankings, you will not get the clients and you will not make the sales you need to stay in business. It’s that simple.
What Is On-Page Optimization?
On Page Optimization, also known as On-page SEO or On-site SEO, refers to the process of optimizing your website and webpages to improve your search engine rankings and earn organic traffic. Above all, your website content must be unique and relevant to the terms searched and show a high level of expertise, authority and trust.
There are many components to a website, both what the user sees and what they don’t see (all the back-end code stuff). Each of these components work together to provide the ultimate result.
If you already have a website and you are looking to improve it, your first step is to head over to Google’s Page Speed Insights. This free tool will provide you a report identifying all the issues or problems with your website. The next step would b to correct each one issue one at a time.
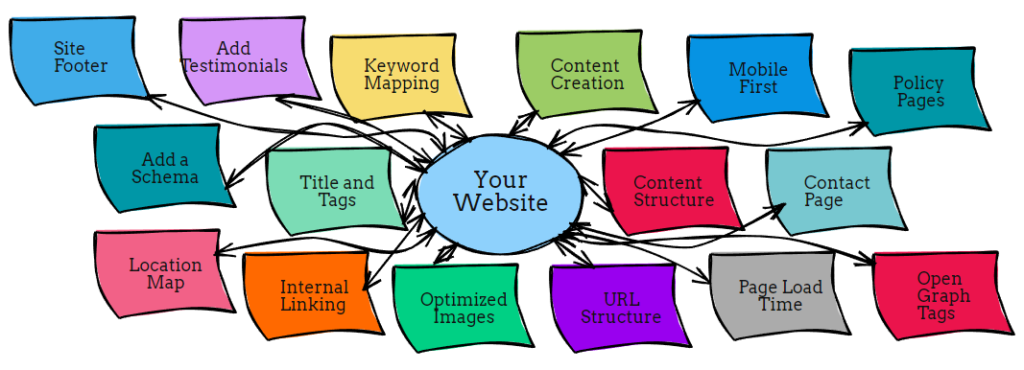
The 16 Key Components of On-Page Optimization
1) Keyword Mapping: Map your target keywords to the individual pages of your website. Ideally, each page will have a target keyword as the page name and used in the body of the page relevant to what the page is about. Avoid keyword stuffing (using too many keywords and/or using too many times on a page).
2) Title and Meta Descriptions: Place your target keywords in the page titles and meta descriptions across your website. Be sure to include a canonical “rel” tag to identify your page as the most representative page for the content.
3) Content Creation: Write informative, keyword-optimized content. Use pages appropriately to explain what your business is about and the services/products you offer. Write with your target audience in mind but be sure to strategically incorporate your target keywords throughout. More on this later.
4) Content Structure: Your webpages to some degree should all be consistent in appearance with each other. You want your users to know they are on the same website as they navigate from page to page. Make sure each webpage has one and only one H1 heading tag with the page title and rest of the page maintains a structure using H2, H3, etc. heading tags.
5) Internal Linking: Add internal links between various pages on your website. These will help users find the information they are looking for and more easily access your important pages. Make sure all links on your site work and take the user to the intended target page.
6) Image Optimization: Include eye-catching images with optimized alt text. Try to include your target keywords, if possible. Reduce the file size of your images to reduce website load time. Use the correct file format (.jpg, .png or .webp). Be sure to use alt tags and title tags when appropriate.
7) URL Structure: Create concise image URLs for all your pages and posts. Ideally, each URL should include the target keyword for that page.
8) Mobile First: Structure your website for mobile users. Google has adopted a policy of mobile first. Sites that do not support mobile users do not rank. Be sure to make your phone number is clickable.
9)Page Load Time: Optimize your pages and content so it loads as quick as possible. Google wants to see less than 4 seconds, less than 3 seconds for mobile.
10) Add a Schema: Schema.org was invented to create a common language between major search engines. It makes it easier for search engines to quickly understand what your website is all about. Use the markup language to tell the search engines you are a local business with specific products. To make this process easier, Hall Analysis has created a tool to help you create your Schema markup. You can then test it using Google’s structured data testing tool.
11) Add Testimonials: Both your customers and Google love testimonials. They are a clear trust signal that serves to not only boost your search results but also helps people feel confident in your business.
12) Map to Your Location: If you have an office or a physical location where a customer can visit and you want them to visit, add a map to your location.
13) Dedicated Contact Page: Make sure you have a dedicated and easy to find contact page. Make sure the page has your NAP+W information (name, address, phone number and website) and your email address. If you have multiple locations, list them all. If you do not have a contact form, consider adding one.
14) Site Footer: Create a consistent site footer and use it on all your webpages. Be sure to include your contact information. This is a great place to add your hours and links to all your pages or sections of your website that may not appear in your menu.
15) Policy Pages: Depending on your business and if you collect any data, you should have at least a Policy page and Terms of Use page. Although these may not have an impact on SEO, they are required if you are doing any sort or paid advertising. Consult legal counsel.
16) Open Graph Tags: Open Graph tags allow your webpages and content to be shared on social media. Once shared, they add an external link back to your site. FreeCodeTools has an easy to use generator. Simply fill out the form, copy and paste into the head section of your website. If you use Twitter, try the Twitter Card Generator too.







